It occurs in the nucleus during the G1 & G2stage of the cell cycle.
Of the two strands of DNA only one strand called the template strand takes part in transcription.
TRANSCRIPTION UNIT:
A transcription unit in DNA consists of three regions:
A promoterThe structural geneA terminator.

Structural gene is the part of DNA from which RNA is formed.
It is polycistronic in prokaryotes and is monocistronic in eukaryotes.
Transcription occurs with the help of DNA dependent RNA polymerase.
Polymerization occurs in 5′ → 3′ direction.
The 3′ → 5′ strand of DNA acts as the template strand/ anti-sense strand.The 5′ → 3′ strand is the coding strand/ sense strand.
All reference points while defining the transcription unit is made with coding strand.
Lying towards 5′ end (upstream) of structural gene is the promoter. It is the binding site for RNA polymerase for transcription to start
Lying towards 3′ end (downstream) of structural gene is the terminator, where transcription ends.
RNA polymerase:
Single RNA polymerase synthesizes all type of RNA in prokaryotes.
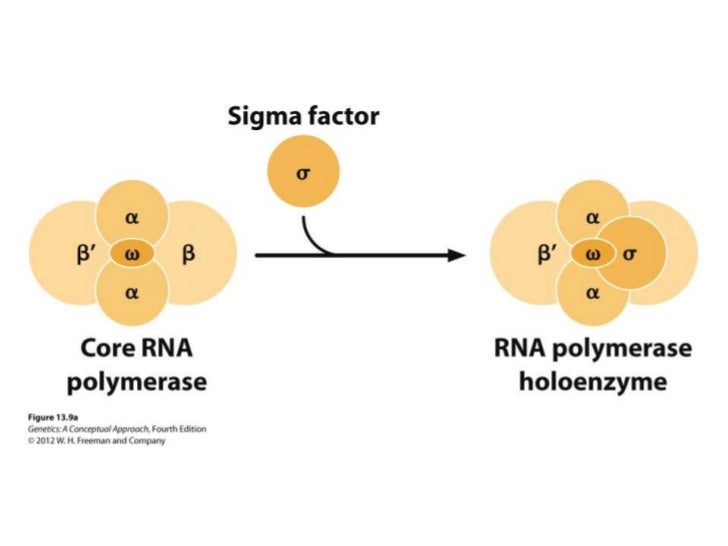
RNA polymerase is a holoenzyme made of 5 polypeptide chains: 2α ( helps in chain initiation and interaction with regulatory proteins ) and , β( catalytic centre - chain initiation and elongation ), β′(Dna binding ) & σ factors.Sigma (σ) factor recognizes the promoter to which RNA polymerase binds and the ‘σ’ factor is released immediately after initiation.RNA polymerase without ‘σ’ factor is core polymerase.
Image source credit -http://www.slideshare.net/paulawaziry/lecture-6-biol3600-transcription-m-rna-processing-winter-2012-pw
There are 3 RNA polymerases in eukaryotes:
- RNA polymerase I synthesizes 28S, 18S & 5.8S rRNAs.
- RNA polymerase II synthesizes hnRNA (heterogeneous nuclear RNA) that forms mRNA.
- RNA polymerase III synthesizes t RNA, 5S rRNA & small nuclear RNAs.
Difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes transcription -
1.Coupled transcription-translation that is called attenuation
is the rule in case of prokaryotes .
is the rule in case of prokaryotes .
Coupled transcription translation is (Eukaryotes )
not possible.
2.Occurs in the cytoplasm.( Prokaryotes )
Occurs in the nucleus. (Eukaryotes )
3.Initiation of transcription does not need any proteins or initiation factors.( Prokaryotes )
Initiation of transcription requires proteins called transcription factors. These are TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE, TFIIF AND TFIIH. These recognise TATA BOX.((Eukaryotes )
4.. Transcription and translation
The process of mRNAProcessing of hnRNA includes:
Addition of 5’cap(7 methylguanosine)
Addition of 3’poly A tail. (Eukaryotes )
5..The 23S, 16S and 5S rRNAs are formed from a single primary transcript. (Prokaryotes)
The 28S, 18S, 5.8S and 5S rRNAS are formed from two primary transcripts.(Eukaryotes)
6. Inhibitors:
(Rifampin: RNA polymerase binds to β subunit.
Actinomycin-Intercalates to interrupt transcription.)- Prokaryotes
Inhibitors:
α amanitin: Inhibits RNA polymerase 2 most srongly- Eukaryotes
Thank you for visiting my blog.Please feel free to share your comment on this
article ,Please subscribe and share the articles to get more such articles.
1.The complex of RNA polymerase, DNA template and new RNA transcript is called-
| ||||||||
Answer: Option A
|
2.Multiple copies of 5S genes, located at a chromosomal site distinct from the other rRNA genes-
| |||||||||||||||||||
Answer: Option A
|
Thank you for visiting my blog.Please feel free to share your comment on this
article ,Please subscribe and share the articles to get more such articles.

No comments:
Post a Comment