The gradual deteriotion of cell division and growth that lead to death is termed as senescence. Telomeres ends serve to protect the coding DNA of the genome. When a telomeres shorten to critical lengths, the cell senescence and die off. It may affect the whole organism or some parts , cells and tissues. In case of leaf it may be seasonal leaf senescence or sequential leaf senescence.
Role of hormones -
- Cytokinin is a plant growth regulator which delays leaf senescence by delaying the degradation of chloroplasts . In the leaf it starts from margin and move towards the interior.
- ABA(Abscissic acid ) induces senescence resulting in chlorosis and necrosis.
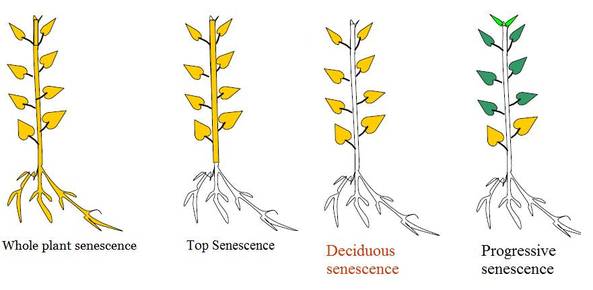
Types of senescence-
1.Whole plant senescence - Found in monocarpic plants .Whose are flower only once in their life cycle .(Annuals and bienneals) In this the senescence process begins with reproductive phase and the whole plant dies after seed formation .(Bamboos)
2.Shoot senescence- The upper part of shoot only undergoes senescence. The underground shoot remains as it is . It is seen in perennial plants . Examples zinger ,Musa paradisica
3.Organ senescence- Occur only in the lateral organs like leaves and fruits . It is of 2 types -
Simultaneous senescence - Seen in deciduous plants where all leaves senesce at a particular season . It is also called as seasonal or deciduous senescence. It is controlled by environmental factors. Example is maple .
Sequential senescence (Progressive) -(Example coleus plant) As the name indicates the senescence occurs in a sequential manner depending upon the age of leaf. The progressive older and lower leaves senesce while the new ones are added to the shoot .
Image source credit -http://biology4isc.weebly.com/7-plant-hormones-and-photomorphogenesis.html
Thank you for visiting my blog.Please feel free to share your comment on this article ,Please subscribe and share the articles to get more such articles.

No comments:
Post a Comment