Cell cycle checkpoints-Cell cycle is a sequential step that taking place in a cell leading to the accurate duplication of genetic materials (DNA). Checkpoints halt the progress of cell cycle if
Image source credit -http://gleesonbiology.pbworks.com/w/page/7537859/C9
(1). G1 checkpoint (restriction checkpoint)
(3). Metaphase (M) checkpoint (spindle assembly checkpoint)
(1) any of the chromosomal DNA is damaged
(2) DNA replication during S phase or chromosome alignment during M phase, have not been properly completed.
Cell cycle checkpoints functions:
- The nuclear genome is intact (without any mutation)
- The conditions are appropriate for a cell to divide (enough nutrients is there for the daughter cells)
- Genetic material is replicated only once in a cell cycle
- No mutations occurred in the replicated chromosomes.If mutations are occurred, these mutations will be rectified by DNA repair system
- Chromosomes are correctly oriented in the metaphase plate
- All chromosomes are correctly attached to the spindle fibres.
The cyclins are so named because their amount varies throughout the cell cycle. To be active, the cyclin dependent kinases (cdks) controlling the cell cycle must bind to a specific cyclin. Cyclins fluctuate during cell cycle.
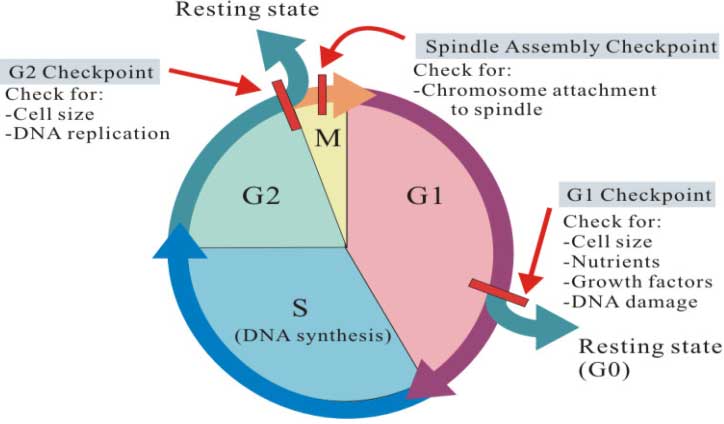
Different types of checkpoints in cell cycle:
There are three checkpoints in a cell cycle.
(1). G1 checkpoint (restriction checkpoint)
(2). G2 checkpoint (G2-M DNA Damage Checkpoint)
(3). Metaphase (M)-checkpoint (Spindle assembly checkpoint)
(1). G1 checkpoint:
G1 checkpoint(restriction point). operates at the end of G1 phase of cell cycle. It checks whether the conditions are favorable for the cell to divide. It also checks the DNA for any damage before it is going for a cycle of DNA replication in the next phase (S phase). If DNA damage is detected, checkpoint proteins will prevent the formation of active cyclin/cdk complexes. Inhibition of cyclin/cdk complex formation stops the progression of the cell cycle. The cells are then direct the DNA repair mechanism to rectify the DNA damage. If the environmental conditions are not good, the cell may enter into G0 phase. In yeast cells, G1 checkpoint is also called as start point.
(2). G2 checkpoint
G2 operates at the end of G2 phase. ( G2-M DNA damage checkpoint.) G2 checkpoint checks the DNA for any damage that might be occurred during the DNA replication in the previous cell cycle phase (S phase). G2 checkpoint also ensures that the entire DNA has been replicated completely. Apart from this, G2 checkpoint monitors the levels of proteins and growth factors that are needed in the next phase (M phase) of cell cycle. If any of the above factors are not satisfactory, the G2 check point hold the cells at G2 phase and initiate machineries to rectify the problems.
(3). Metaphase (M) checkpoint (spindle assembly checkpoint)
Metaphase checkpoint is also called as spindle assembly checkpoint. It operates at the end of M phase. Metaphase checkpoint senses the integrity of the spindle apparatus in the cell. Spindle apparatus is involved in sorting of chromosomes during cell division. Correct orientation of chromosomes in the metaphase plate of cell is very essential for the proper segregation of chromosomes. If chromosomes are not correctly attached to the spindle apparatus, the metaphase checkpoint will stop the cell cycle. Thus, M checkpoint prevents cells from incorrectly sorting their chromosomes during division.So, M-Cdk inhibits mitosis .
Importance of cell cycle checkpoints-
- They can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) .
- Cell cycle checkpoint ensure only one round replication of DNA per cell cycle.
- Almost all cancers are due to the improper functioning of either one or many proteins involved in cell cycle regulation. (Eg. P53 – guardian of genome, a tumor suppressor gene).
Q.1 Tyr-15 is dephosphorylatedby ?
a. cdc25
b. cdc2
c. Both
d. Cdk1
And. A
Q2.When cell has stalled DNA replication fork, which checkpoint should be predominantly activated?
A)M
B)Both G¹M and M
C)G¹/S
D)G²/M
Ans.D
Q2.When cell has stalled DNA replication fork, which checkpoint should be predominantly activated?
A)M
B)Both G¹M and M
C)G¹/S
D)G²/M
Ans.D
Thank you for visiting my blog.Please feel free to share your comment on this article ,Please subscribe and share the articles to get more such articles.

No comments:
Post a Comment