Thank you for visiting my video tutorial/ blog.Please feel free to share your comment on this
article ,Please subscribe and share the articles to get more such articles.
| Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay | ||||
| Immunoprecipitation | ||||
| Single radial immunodiffusion (RID) assay | ||||
| Immunoelectrophoresis Ans. c 4.The quantitative technique where a negatively charged antigen is electrophoresed into a gel containing antibody is- a.RDI (Radial immuno duffusion) b.Mancini method c.Double diffusion d.Both a and b Ans.d Thank you for visiting my video tutorial/ blog.Please feel free to share your comment on this
article ,Please subscribe and share the articles to get more such articles.
| ||||
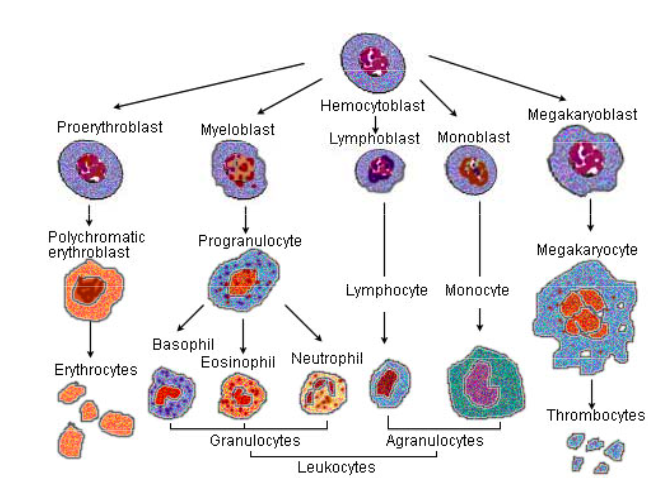 Image source credit -https://www.wikipremed.com/image.php? img=040706_68zzzz373750_Illu_blood_cell_lineage_68.jpg&image_id=373750
Image source credit -https://www.wikipremed.com/image.php? img=040706_68zzzz373750_Illu_blood_cell_lineage_68.jpg&image_id=373750
In monoclonal antibody technology, tumor cells that can replicate endlessly are fused with mammalian cells that produce an antibody. The result of this cell fusion is a
| ||||||||||||||||
Ans. A
5.Hybridomas are produced by combining with- a.B cell and Myeloma cells b.B cell with particular epitopes c.Both a and b d.None of the above ans.a 6.
| ||||||||||||||||
| Agglutinogen in a viral hemagglutination test- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
b.Antigens c.WBC d.RBC Ans.d 2.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
a) naive B cellsAns.b
b) Memory cells
c) naive T cells
d) NK cells